The U.S. innovation ecosystem stands as a beacon of progress and ingenuity, influencing countless sectors, particularly health technology innovation. Rooted in the strategic investments made during World War II, this ecosystem has cultivated groundbreaking advancements, especially in biomedical research. Government-driven public-private partnerships have played a pivotal role in creating a robust landscape for scientific discovery, underpinned by substantial federal funding for research. Over the decades, this collaborative model has led to remarkable breakthroughs, from the mass production of penicillin to the latest advancements in drug development. As a result, the U.S. has not only transformed medical care domestically but has also positioned itself as a global leader in health innovation, setting a standard that many countries aspire to emulate.
The landscape of U.S. technological advancement, often described as a thriving innovation hub, has its roots deeply embedded in strategic government initiatives. This dynamic environment, characterized by collaborative efforts between public entities and private enterprises, has fostered significant improvements in various fields, especially within the realm of healthcare technology. Initiatives funded by federal agencies have consistently propelled the nation’s research endeavors, leading to critical evolutions in biomedical advancements. As seen during pivotal moments such as World War II, these collaborations have not only yielded essential medical breakthroughs but have also laid the groundwork for a sustained culture of innovation. In essence, this interconnected framework of academic, governmental, and industrial spheres exemplifies the unique synergy that drives U.S. innovation forward.
The Origins of the U.S. Innovation Ecosystem
The U.S. innovation ecosystem has its roots in the urgent technological demands of World War II. Prior to the war, the American military lagged in technological advancements, prompting a unique collaboration between academia, industry, and government. This partnership catalyzed a wave of innovations that would not only help the U.S. and its allies win the war but would also lay the groundwork for decades of progress in fields such as biomedical research and health technology innovation. Game-changing advancements like the mass production of penicillin emerged from this collaborative model, showcasing the effectiveness of federal funding in stimulating research and development.
As the war advanced, the establishment of entities such as the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD) highlighted the critical role of public-private partnerships in tackling pressing scientific challenges. The backing provided by the federal government enabled university laboratories and industrial research facilities to mobilize resources and talent quickly, achieving breakthroughs in medicine that have reshaped public health. This foundational period marked the beginning of a sustainable innovation ecosystem that would continue to evolve post-war.
Public-Private Partnerships: A Pillar of Innovation
Public-private partnerships have been central to the U.S. innovation ecosystem, particularly in the realm of biomedical research. The collaboration between government entities, academic institutions, and private firms fosters an environment where resources, knowledge, and technology can be shared to address complex health challenges. By pooling expertise and funding, these partnerships have led to significant advancements in health technology innovation, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in medical treatments and disease prevention.
Historically, these collaborations have thrived under frameworks created during World War II. The research and development networks established during this period paved the way for more structured partnerships that prioritize both clinical and commercial objectives. Such frameworks have proven essential in securing federal funding for research, which remains critical for advancing new therapies and medical devices. As challenges in healthcare become increasingly sophisticated, the need for continued public and private sector collaboration remains paramount.
The Role of Federal Funding in Biomedical Research
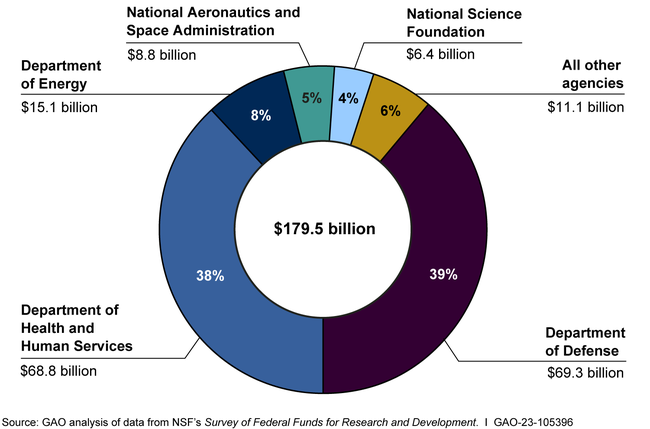
Federal funding for research has been a cornerstone of the U.S. innovation ecosystem, particularly in advancing biomedical research. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is a prime example of how government investment can stimulate groundbreaking discoveries and foster a robust research landscape. By providing grants and funding opportunities, the NIH has empowered countless researchers to explore innovative therapies and conduct pivotal studies that have transformed public health over the decades.
However, recent discussions about capping reimbursement for indirect research costs have raised concerns regarding the future of federal support. Critics argue that any reduction in funding could jeopardize the progress made in fields that rely heavily on sustained investments. It is essential for stakeholders—including policymakers, researchers, and industry leaders—to recognize the critical relationship between federal funding and continued success in biomedical research, a fundamental aspect of maintaining the United States’ standing as a leader in global health.
Impact of World War II on Health Technology Innovation
World War II catalyzed an unprecedented wave of health technology innovation, primarily through the intense collaboration and resource mobilization seen during this time. With the military’s pressing need for medical advancements, federal and private partnerships were forged to address health challenges that posed risks to soldiers on the battlefield. The successful development and mass production of penicillin serve as a testament to the rapid innovation that occurred due to wartime urgency.
The methodologies and systems established during the war directly influenced the landscape of health technology innovation in subsequent years. The collaboration fostered by wartime research efforts not only accelerated the pace of biomedical advancements but also laid the groundwork for postwar efforts that improved civilian health. The innovations developed during this period have continued to resonate in today’s biomedical landscape, demonstrating the enduring impact of wartime research on contemporary health technologies.
The Transformative Power of the Office of Scientific Research and Development
The Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD) played a transformative role in shaping the U.S. innovation ecosystem during and after World War II. By coordinating wartime scientific research, the OSRD directly contributed to substantial breakthroughs in health and military technology, fostering a culture of collaboration between the federal government, universities, and industrial laboratories. The establishment of the OSRD exemplified a new model of scientific management that was responsive and adaptive to urgent national needs.
This organization not only facilitated the successful development of vital medical innovations but also instituted policy changes that would have lasting implications for research funding, including support for indirect costs. OSRD’s practices influenced how partnerships are structured today, establishing a framework that emphasizes collaborative R&D efforts. As the U.S. navigates the complexities of contemporary health challenges, the legacy of the OSRD serves as a reminder of the importance of fostering innovative partnerships.
Advancements in Drug Development Post-War
Following World War II, the advancements in drug development that emerged were largely attributable to the robust research environment established during the war. The urgent need for medical breakthroughs resulted in the formulation of new treatments and drugs that addressed both military and civilian health issues. The foundation laid by wartime research led to the antibiotic revolution, drastically improving treatment options for infectious diseases.
Today, the framework for drug development continues to be influenced by the methodologies established in the postwar period. Pharmaceutical companies have built upon the scientific insights and techniques developed during that era to innovate therapies that cater to a diverse range of health challenges. As we witness new breakthroughs in drug discovery, the historical context of wartime research reminds us of the importance of a cooperative research culture that spans government, academia, and industry.
Training the Next Generation of Scientists
The legacy of World War II extends beyond technological advancements; it also encompasses the creation of a comprehensive training environment for a new generation of scientists. This period witnessed an influx of research funding that not only engaged seasoned scientists but also provided invaluable opportunities for thousands of graduate students and emerging researchers. Through their involvement in wartime projects, many young scientists honed their skills and gained hands-on experience that would shape their future contributions to biomedical research.
The importance of training cannot be overstated, as today’s scientific advancements are directly linked to the expertise cultivated during that pivotal time. Initiatives that support professional development and research opportunities for emerging scientists remain essential for maintaining the momentum of innovation in the U.S. innovation ecosystem. Ensuring a continuous pipeline of trained scientists will be vital as we face increasingly complex health challenges in the future.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Current Innovation Landscape
As the U.S. innovation ecosystem continues to evolve, it faces new challenges that require careful navigation. Amidst discussions surrounding federal funding and public-private partnerships, the necessity to sustain and enhance the cooperative framework established during World War II has become increasingly apparent. Policymakers must recognize the crucial role that federal R&D funding plays in fostering breakthroughs that advance our understanding of health and disease.
Moreover, as the global landscape shifts, the U.S. must strive to remain a leader in health technology innovation. This involves addressing current barriers, such as regulatory hurdles and funding uncertainties, while continuing to invest in collaborative initiatives that harness the strengths of both public and private sectors. By embracing these challenges as opportunities for growth, the U.S. can ensure that it maintains its stature as a beacon of innovation in the biomedical realm.
Future Prospects for the U.S. Innovation Ecosystem
Looking ahead, the prospects for the U.S. innovation ecosystem appear promising, provided that the lessons learned from historical partnerships continue to inform current endeavors. The momentum generated during World War II serves as a vital reminder of the potential that arises from collaboration among government, academia, and industry. As new fields of biomedical research emerge, it will be important to adapt existing frameworks to meet contemporary challenges.
Investment in research infrastructure, as well as policies that support collaboration and innovation, will be critical in maintaining the U.S.’s competitive edge. Reinforcing the connection between federal funding, academic research, and private development will create an environment where groundbreaking discoveries can flourish. By focusing on sustainable partnerships and adapting to evolving needs, the U.S. can continue to lead in health technology innovation for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
How has the U.S. innovation ecosystem evolved since World War II?
The U.S. innovation ecosystem has significantly evolved since World War II, originating from government-supported research that contributed to breakthroughs like penicillin production. This partnership among federal agencies, universities, and the pharmaceutical industry established a model for biomedical research that has fueled countless advancements in health technology innovation.
What role do public-private partnerships play in the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
Public-private partnerships are crucial to the U.S. innovation ecosystem, as they foster collaboration between government and private entities. These partnerships have been instrumental in advancing biomedical research and health technology innovation, enabling the seamless transfer of knowledge and funding that drives scientific progress.
What impact does federal funding for research have on the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
Federal funding for research plays a vital role in sustaining the U.S. innovation ecosystem, especially in biomedical research. It supports academic institutions and private companies, enabling them to develop new technologies and treatments. The continuous influx of federal funds has catalyzed significant advancements and discoveries in health technology.
How did World War II research advances shape the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
World War II research advances laid the groundwork for the current U.S. innovation ecosystem by highlighting the importance of a coordinated efforts among federal entities, academia, and private industry. The need for rapid technological solutions accelerated the development of biomedical research and established a framework that continues to drive innovation.
What changes are being debated regarding federal funding for biomedical research?
Currently, there is a debate regarding potential caps on reimbursement for indirect costs in biomedical research, which could lead to cuts in federal funding. This issue raises concerns about maintaining the U.S. innovation ecosystem that relies heavily on public-private partnerships to facilitate advancements in health technology.
Why is the U.S. innovation ecosystem considered the envy of the world?
The U.S. innovation ecosystem is regarded as the envy of the world due to its history of successful collaborations among government, academia, and industry, particularly in biomedical research. This system has produced groundbreaking health technologies and life-saving treatments, positioning the U.S. at the forefront of global innovation.
| Key Points |
|---|
| The U.S. innovation ecosystem in health is globally recognized for its success and collaboration. |
| The partnership between the federal government and academia began during World War II, initially aimed at military technology development. |
| Key advancements, such as the mass production of penicillin, emerged from this partnership, addressing urgent wartime needs. |
| This collaboration laid the foundation for a thriving biomedical sector, enhancing capabilities in drug discovery and medical research. |
| Ongoing debates over federal funding for research highlight the necessity of maintaining this partnership for future innovations. |
| The U.S. innovation system supports sectors beyond biomedicine, influencing defense, health, and economic growth. |
Summary
The U.S. innovation ecosystem has become a global leader in healthcare advancements, driven by a unique public-private partnership that began during World War II. This collaboration fostered significant breakthroughs, such as the mass production of penicillin, and has continued to facilitate substantial progress across various fields. Ongoing scrutiny of federal funding emphasizes the importance of sustaining this ecosystem to ensure continued innovation for national and global benefits.