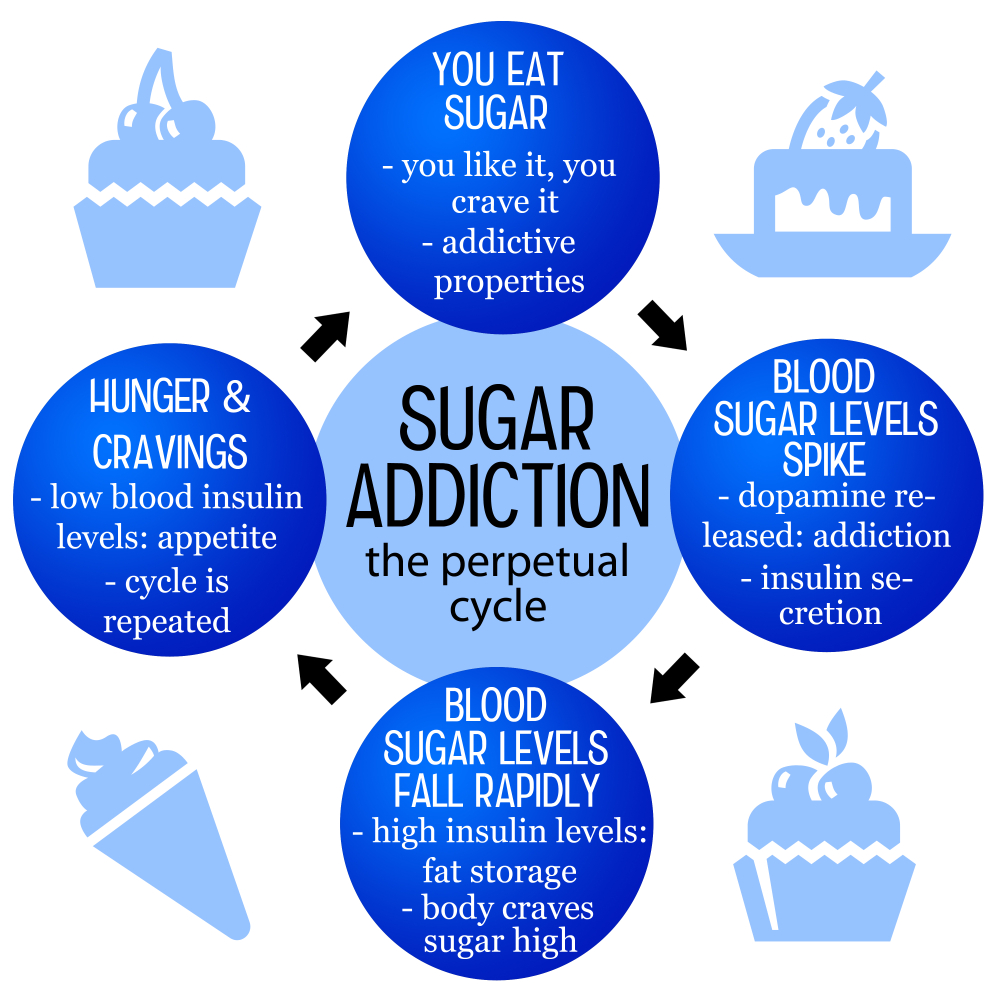
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked a heated debate among nutrition researchers and health professionals alike. While substances like alcohol and nicotine fall under strict clinical definitions of addiction, sugar presents a different puzzle. Many people experience overwhelming sugar cravings, often leading to compulsive eating behaviors that mimic addictive patterns. With the average American consuming nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, it’s crucial to understand the health effects of sugar, especially in terms of sugar consumption’s impact on our diet and overall well-being.
When discussing whether sugar might be classified as addictive, it’s important to note that many refer to the phenomenon as sugar dependence or sugary food cravings. Such discussions often delve into how the consumption of sweetened foods can trigger behavior patterns similar to those seen in traditional addictive substances. This pattern of indulgence highlights the psychological and physical allure of sugar, often reinforced by our food systems loaded with ultra-processed options. Additionally, the relationship between sugar intake and habitual eating behaviors draws attention to broader dietary impacts, making it essential to explore the long-term implications of sugar-laden diets on physical health.
Understanding Sugar Cravings and Their Impact on Health
Sugar cravings are a common experience for many individuals, often resulting from the consumption of ultra-processed foods laden with added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium. These ingredients create a highly palatable product that can lead to habitual consumption. Nutrition experts emphasize that while sugar may not meet the strict criteria for addiction like substances such as nicotine or alcohol, the cravings experienced by consumers can be intense. When these foods are suddenly eliminated from the diet, individuals may encounter withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches, irritability, and fatigue. Understanding these cravings is crucial in managing one’s sugar consumption and promoting healthier eating habits.
Managing sugar cravings effectively requires a careful approach. It is essential to recognize that some level of sugar is needed in our diets, as it enhances flavor and can contribute to overall satisfaction with meals. However, to mitigate harmful health effects associated with excessive sugar consumption, individuals must focus on moderation. For those who consistently consume high levels of sugar, gradual reductions may be more beneficial than abrupt eliminations. This strategy helps avoid the overwhelming feelings of withdrawal while still progressively moving towards healthier dietary choices.
The Question: Is Sugar Addictive?
The question “Is sugar addictive?” elicits significant debate among health professionals. While alcohol, nicotine, and illicit drugs are classified as addictive substances due to their severe withdrawal symptoms and potential for abuse, sugar presents a different scenario. Research indicates that sugar can influence the brain’s reward system, leading to increased cravings and compulsive behaviors similar to those seen with addictive drugs. However, the physical and psychological effects of sugar do not reach the same severity levels as those associated with traditional addictive substances, complicating the classification of sugar as an addictive item.
It’s crucial to differentiate between cravings induced by sugar and those related to addictive substances. While some individuals may experience strong urges or compulsive patterns of sugar consumption, the physiological need for sugar differs from that of narcotics. Sugar occurs naturally in many foods that are necessary for life, such as fruits and vegetables. Dietitians recommend focusing on balanced nutrition rather than labeling sugar as purely addictive; moderation, mindful consumption, and attention to overall health effects are vital to maintaining a healthy relationship with sugar.
Health Effects of Excessive Sugar Consumption
Excessive sugar consumption is a significant public health concern, linked to various negative health outcomes. The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar intake to no more than six teaspoons per day for women and nine for men. However, the average American consumes nearly 20 teaspoons daily, primarily from sugary beverages and snacks, contributing to obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. These health effects underscore the importance of monitoring sugar intake and understanding its broader impact on overall wellness.
To mitigate the health effects of sugar, individuals should focus on adopting a balanced diet rich in whole foods. Incorporating fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help reduce cravings for sugary snacks. Additionally, reading food labels and being aware of hidden sugars in processed foods can empower consumers to make healthier choices. Educating oneself about the health effects of sugar and implementing gradual changes in dietary habits can lead to improved health outcomes and a reduction in sugar-related cravings.
Strategies for Reducing Sugar in Your Diet
Reducing sugar intake can seem daunting, but several strategies can simplify the process. One effective approach is to gradually decrease added sugars rather than cutting them out entirely. This method helps to prevent withdrawal symptoms that can arise from sudden changes in diet. Start by identifying high-sugar items in your pantry, such as sodas or sugary snacks, and replace them with healthier alternatives. Opt for flavored water instead of soda, and choose fruit or yogurt for dessert. Over time, these small changes can significantly lower overall sugar consumption.
Another beneficial strategy is to plan meals and snacks to ensure that they are balanced and filled with nutrient-dense foods. Preparing meals at home allows for greater control over ingredients, as well as the sugar content. Incorporating more whole foods like vegetables, beans, and whole grains not only decreases sugar intake but also increases fiber and essential nutrients, leading to greater satisfaction and reduced cravings. Finally, being mindful of portion sizes can also help manage sugar consumption without extreme restriction, making the process of reducing sugar a healthier and more sustainable journey.
The Role of Sugar in a Balanced Diet
Sugar, when consumed in moderation, can play a role in a balanced diet. Natural sugars found in fruits, vegetables, and dairy products provide essential nutrients and energy, contributing to overall dietary satisfaction. These sources of sugar, unlike added sugars found in processed foods, come with beneficial fibers, vitamins, and minerals. Thus, understanding the distinction between natural and added sugars is crucial for making informed dietary choices that promote health.
It’s essential to recognize that while sugar can enhance flavor and satisfaction in food, its consumption should be approached thoughtfully. Integrating a variety of whole foods into one’s diet can create a more rounded, nutrient-dense eating plan, minimizing the negative health effects associated with excessive added sugar. Hence, achieving balance involves not only managing sugar intake but also emphasizing whole, nutritious foods that contribute to better health outcomes and a more enjoyable eating experience.
Long-Term Effects of Sugar on Mental Health
Emerging research suggests a link between sugar consumption and mental health. High sugar intake has been associated with increased risks of mood disorders, anxiety, and depression. The brain’s reward center responds to sugar in a way that can create a cycle of craving and bingeing, which may contribute to feelings of guilt and distress. Addressing sugar consumption, therefore, should not only focus on physical health but also mental well-being.
To support mental health, strategies such as mindfulness in eating and reducing sugar-laden foods can be essential. Incorporating more whole foods and balanced meals can help stabilize energy levels and mood. Furthermore, seeking out alternatives to sugar, such as satisfying snacks rich in protein or healthy fats, can contribute positively to one’s emotional state. Awareness of the mental health implications of sugar can lead to more mindful choices that support overall well-being.
Sugar’s Connection to Obesity and Weight Management
The connection between sugar consumption and obesity is widely acknowledged in the health community. Excessive sugar intake, particularly from sugary beverages, significantly contributes to weight gain and obesity rates. The high caloric content of sugary products, combined with their low nutritional value, creates an imbalance that leads to weight management challenges. Understanding this link is crucial for individuals looking to maintain or achieve a healthy weight.
To effectively manage weight, individuals should focus on reducing added sugars in their diet. Implementing strategies such as portion control, mindful eating, and swapping sugary snacks for healthier alternatives is essential. Incorporating regular physical activity can also help offset the effects of sugar consumption. Overall, a comprehensive approach that addresses both diet and lifestyle can aid in achieving and maintaining a healthy weight while mitigating the risks associated with excessive sugar intake.
The Impact of Sugar on Children’s Health
Children are particularly vulnerable to the health effects of excessive sugar consumption. High sugar intake can lead to developmental issues, childhood obesity, and increased risk for chronic diseases later in life. Furthermore, sugary snacks can impact children’s energy levels and behavior, resulting in mood swings and difficulty concentrating. Educating parents about appropriate sugar consumption for children is vital in fostering healthy habits from a young age.
To promote healthier eating patterns among children, parents can encourage balanced meals with minimal added sugars. Involving children in meal planning and preparation can increase their interest in healthy foods. Additionally, creating a balanced snack environment at home, emphasizing fruits, nuts, and whole grains, can help children develop a preference for nutritious choices over sugary snacks. Ultimately, early intervention and education regarding sugar intake can set the foundation for a healthier future.
Navigating Social Situations and Sugar Consumption
Navigating social situations can be challenging for those trying to reduce sugar intake. From birthday parties to holiday gatherings, the abundance of sugary foods can tempt individuals to indulge. Effective strategies for handling these situations include preparing in advance by eating a healthy meal beforehand or bringing a nutritious snack to share. Understanding one’s triggers in social settings can empower individuals to make conscious choices that align with their health goals.
Moreover, communicating dietary preferences to friends and family can foster support and understanding. By openly discussing health choices, individuals can create an environment that encourages healthier behaviors. Practicing moderation, rather than complete avoidance, allows for balanced participation without feeling deprived. Ultimately, successfully navigating social situations involves finding a middle ground between enjoying social interactions and maintaining a commitment to reducing sugar consumption.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like alcohol or nicotine?
While sugar can stimulate cravings and compulsive eating behaviors akin to addictive substances, it is not officially classified as an addictive substance in the same way as alcohol or nicotine. The effects of sugar can lead to habitual consumption, but with moderate intake, severe withdrawal symptoms are unlikely.
What causes sugar cravings and how can I control them?
Sugar cravings often stem from the consumption of ultra-processed foods high in added sugars. To control these cravings, gradually reduce sugar intake rather than quitting cold turkey. This method helps to mitigate withdrawal-like symptoms and promotes healthier eating patterns.
What are the health effects of sugar consumption?
Excessive sugar consumption is linked to various health issues, including obesity and chronic diseases. The American Heart Association advises limiting added sugar to no more than 9 teaspoons for men and 6 teaspoons for women to minimize these health risks.
How does sugar impact my diet and overall health?
Sugar plays a dual role in diet; while it enhances flavor and enjoyment, excessive sugar intake can lead to negative health effects. A balanced approach with controlled sugar consumption is essential to maintaining health and preventing issues related to addictive behaviors.
Can reducing sugar help with addictive behaviors?
Yes, reducing sugar intake can alleviate some addictive behaviors associated with cravings. By lowering sugar gradually, individuals can diminish withdrawal symptoms and develop healthier eating habits, ultimately improving overall well-being.
Is it possible to eliminate sugar completely from my diet?
Eliminating sugar completely isn’t practical since it’s naturally present in many foods like fruits and dairy. Instead, focus on moderate consumption of added sugars and be mindful of labels to maintain a balanced diet.
What strategies can help with sugar addiction in my diet?
To address sugar addiction, practice moderation by gradually reducing added sugars instead of sudden withdrawal. Choose whole foods, read labels carefully, and replace sugary snacks with healthier options to cultivate a more balanced diet.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Cravings exist | Cravings for sugar are real but classifying sugar as addictive alongside substances like alcohol and nicotine is debated. |
| Not officially addictive | Sugar increases cravings and compulsive behaviors, but it doesn’t meet the strict clinical criteria for addiction. |
| Health implications | Excessive sugar consumption contributes to health issues; moderation is key for a balanced diet. |
| Average consumption | The average U.S. adult consumes nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, significantly exceeding recommended limits. |
| Gradual reduction advice | It’s better to gradually decrease added sugar intake rather than completely stopping abruptly. |
| Nutritional necessity | Unlike drugs that can be eliminated from the diet, sugar in moderate amounts is essential in various foods. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked much debate within the nutrition community. While sugar can lead to cravings similar to those of addictive substances, it is not classified as addictive by current clinical standards. Unlike drugs or alcohol, sugar is naturally present in many healthy foods, and moderate consumption does not typically result in negative health consequences. Therefore, understanding the role of sugar in our diets is crucial, encouraging moderation rather than outright elimination.