Suicide prevention for older adults is a crucial yet often overlooked aspect of mental health resources. This vulnerable population, especially those aged 75 and older, faces significant risks related to loneliness, chronic illnesses, and a lack of accessible support systems. Recent studies reveal a startling gap in suicide prevention strategies specifically catered to aging individuals, underscoring the importance of targeted outreach. Issues like social isolation and inadequate representation in healthcare research exacerbate older adults’ suicide risk, making it essential for organizations to mobilize effective, age-appropriate resources. By harnessing the power of online health information, we can create comprehensive interventions that address the unique healthcare needs of our elderly population, thus fostering a supportive environment for mental well-being.
When discussing the critical need for mental health support aimed at seniors, we can refer to this issue as elder suicide prevention. It’s alarming to note that individuals in their later years, particularly those over 75, display some of the highest suicide rates compared to other demographics. Enhanced attention to their mental wellbeing is essential, given that systemic biases often leave them without proper assistance. Effective prevention strategies tailored to older adults could make a significant difference by reducing the stigma surrounding mental health in this age group and fostering connections within communities. By emphasizing dedicated resources and outreach, we can help mitigate the growing crisis among our aging population.
Understanding the High Suicide Risk Among Older Adults
Older adults, especially those aged 75 and above, are at a uniquely high risk for suicide, with statistics revealing alarming trends in mental health among this demographic. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, this age group has a suicide rate of 20.3 per 100,000, which starkly contrasts with younger populations that have seen declines in their suicide rates. The reasons behind these disturbing figures are multifaceted, encompassing factors such as social isolation, psychological distress, and a lack of access to adequate mental health resources.
Moreover, systemic issues such as ageism contribute to the invisibility of older adults in mental health discourse, further complicating their access to necessary support. Many older adults facing suicidal thoughts may not readily identify as needing help, leading to underdiagnosis and fewer individuals seeking assistance. Thus, improved suicide prevention strategies that include tailored communication and outreach are essential to address the unique healthcare needs of older adults.
The Necessity of Tailored Suicide Prevention Strategies
Current suicide prevention strategies often overlook older adults, focusing predominantly on younger populations who are deemed more at risk. However, experts in geriatric psychiatry emphasize the urgent need for strategies specifically tailored to older adults. This can include public campaigns designed to resonate with older individuals, highlighting the importance of community engagement and social connection in mitigating feelings of loneliness and despair. Such approaches not only help in lowering suicide rates among older adults but also promote overall mental well-being within this vulnerable population.
Importantly, the effectiveness of these tailored campaigns heavily relies on collaboration between mental health professionals and established organizations. By leveraging resources from geriatric psychiatry and mental health advocacy groups, there is potential to craft interventions that are both effective and accessible. Utilizing online platforms where many older adults seek health information can provide a critical channel for disseminating this information, ensuring it reaches those who need it most.
Navigating Online Health Information for Older Adults
In today’s digital age, older adults are increasingly turning to the internet for health information, including mental health resources. However, a study conducted by researchers at McLean Hospital indicates that these individuals often encounter barriers when searching for relevant suicide prevention resources. Of the organizations studied, very few provided content specifically aimed at older adults, indicating a significant gap in online support. This underrepresentation can leave many older adults feeling unsupported and isolated when they seek help.
To effectively bridge this gap, organizations must prioritize the creation of user-friendly online resources that cater specifically to older demographics. This includes simplifying language, ensuring navigability, and providing culturally relevant information. Furthermore, integrating resources for older adults into broader public health campaigns can promote awareness and help guide individuals toward mental health assistance when needed.
Exploring Mental Health Resources for Older Adults
Access to mental health resources is crucial for suicide prevention in older adults, yet many face challenges in obtaining such support. The lack of comprehensive and accessible resources targeting this demographic can perpetuate feelings of hopelessness and despair. To address these challenges, organizations must highlight existing resources and improve their visibility online. This could include partnerships with healthcare providers who can recommend mental health services to older patients or caregivers looking for support.
Moreover, integrating mental health education into senior centers, community programs, and local healthcare systems can create a more supportive environment for older individuals. By actively promoting mental health literacy, these initiatives can empower older adults and caregivers with the knowledge necessary to recognize the signs of distress and seek help effectively. Investing in these mental health resources not only aids in prevention but also fosters a more understanding and proactive community.
The Role of Geriatric Psychiatry in Suicide Prevention
Geriatric psychiatry plays a vital role in addressing the unique mental health challenges faced by older adults, particularly in the context of suicide prevention. Clinicians specializing in this field are trained to recognize and respond to the complex factors contributing to suicidal ideation in older adults. By fostering a deeper understanding of mental health issues within this group, geriatric psychiatrists can lead the way in developing targeted interventions and support systems that address their specific needs.
Moreover, collaboration with organizations focused on suicide prevention can enhance the effectiveness of strategies employed. By integrating the expertise of geriatric psychiatrists into public-facing campaigns and community programs, we can create a robust support network that not only addresses immediate needs but also promotes long-term mental health and wellness among older adults.
Utilizing Online Platforms to Raise Awareness
Online platforms represent a powerful tool for raising awareness about the suicide risk faced by older adults. As mentioned previously, many older adults turn to the internet for information, making it essential for organizations to utilize these platforms to reach this demographic effectively. Social media campaigns, informative websites, and online support groups can all play a significant role in bridging the information gap and providing accessible resources.
These platforms can also facilitate community engagement, allowing older adults to connect with one another and reduce feelings of isolation. Encouraging dialogue around mental health in these online spaces can help normalize discussions about suicide risk and encourage those in need to seek help. As we continue to harness the power of technology, it’s critical to ensure that the content shared is relevant and sensitive to the needs of older adults.
The Importance of Research Funding in Geriatric Psychiatry
Sustaining and expanding research into late-life suicide prevention is critical to understanding and addressing the unique challenges faced by older adults. However, funding for research in geriatric psychiatry is often limited, resulting in gaps in our knowledge and resources for this vulnerable population. Increased investment in this field will allow for more extensive studies aimed at identifying effective suicide prevention strategies that cater specifically to older adults and their mental health needs.
Funding from sources such as the National Institute on Aging and the National Institute of Mental Health can significantly contribute to breakthroughs in understanding the aging population’s mental health. These financial resources can support innovations in care models, research on the efficacy of different interventions, and the development of tailored programs that can be implemented at local and national levels, ultimately leading to a decline in suicide rates among older adults.
Community Engagement as a Key Element of Prevention
Community engagement is paramount in creating effective suicide prevention strategies for older adults. Initiatives that encourage social connectivity can significantly reduce feelings of isolation and loneliness, which are often at the root of suicidal thoughts. Programs designed to foster interaction among older adults—such as social clubs, volunteer opportunities, and community events—can provide essential support networks and resources that promote mental well-being.
Furthermore, training community members and leaders in recognizing the warning signs of depression and suicidality in older adults can empower them to respond appropriately and compassionately. By fostering a supportive community environment, we not only enhance the quality of life for older adults but also create a proactive approach to mental health support, ultimately reducing suicide rates and improving overall health outcomes.
The Role of Caregivers in Suicide Prevention for Older Adults
Caregivers play a crucial role in the lives of older adults, often being the first individuals to notice changes in behavior or mood that may indicate a decline in mental health. As such, it’s essential to equip caregivers with the knowledge and resources needed to recognize the signs of suicidal ideation and understand how to initiate conversations about mental health with their loved ones. This training not only empowers caregivers but also strengthens the support network surrounding older adults.
Furthermore, establishing support groups for caregivers can provide them with a much-needed outlet and resource for discussing their experiences and challenges. Addressing the mental health of those who care for older adults is vital, as caregivers often experience high levels of stress and burnout, which can impact their ability to provide effective support. By nurturing the well-being of caregivers, we can indirectly enhance the overall mental health and safety of older adults in their care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some effective suicide prevention strategies for older adults?
Effective suicide prevention strategies for older adults include regular mental health screenings, promoting social engagement, and providing access to mental health resources tailored to their needs. Community outreach programs and education on recognizing signs of depression and suicidal thoughts can significantly contribute to reducing suicide risk.
How does social isolation impact older adults’ suicide risk?
Social isolation is a significant factor contributing to the elevated suicide risk among older adults. Feelings of loneliness and lack of support can exacerbate mental health issues, making suicide prevention efforts focused on enhancing social networks vital for this age group.
What mental health resources are available specifically for older adults?
Mental health resources for older adults include hotlines, local counseling services, and online platforms offering teletherapy. Organizations like the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) and the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) provide directories for finding age-appropriate mental health support.
Why is there a need for more targeted suicide prevention efforts for older adults?
There is a pressing need for targeted suicide prevention efforts for older adults because they experience higher suicide rates compared to younger age groups. Many public campaigns often overlook this demographic, emphasizing the importance of tailored strategies to address their unique mental health and social needs.
How can geriatric psychiatry contribute to suicide prevention for older adults?
Geriatric psychiatry plays a crucial role in suicide prevention for older adults by specializing in the mental health issues prevalent in this age group. Professionals in this field can develop personalized treatment plans, highlight risk factors, and implement preventive measures that align with the healthcare needs of older adults.
What role does online health information play in suicide prevention for older adults?
Online health information serves as a valuable resource for older adults seeking suicide prevention support. However, accessibility and usability are critical; therefore, it’s essential for sites providing this information to be age-friendly, ensuring that older adults can easily navigate and find the resources they need.
How can family members help with suicide prevention for older adults?
Family members can play an essential role in suicide prevention for older adults by promoting open communication about mental health, encouraging their loved ones to engage in social activities, and helping them access mental health resources. Being attentive to signs of depression or suicidal thoughts can also make a significant difference.
Are there specific signs that indicate an older adult may be at risk for suicide?
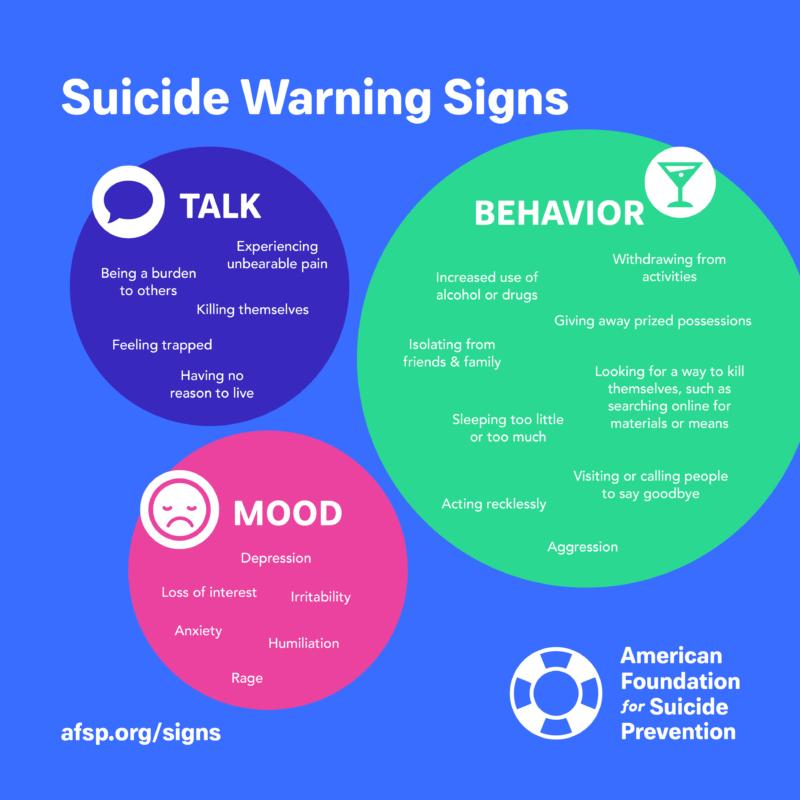
Yes, signs that an older adult may be at risk for suicide include withdrawal from social activities, expressed feelings of hopelessness or worthlessness, changes in appetite or sleep patterns, and giving away personal belongings. Recognizing these indicators can prompt timely intervention and access to mental health support.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| High Risk Population | Older adults aged 75 and above have the highest rates of suicide at 20.3 per 100,000. |
| Lack of Resources | National suicide prevention organizations provide few resources specifically for older adults. |
| Imbalance in Efforts | Online resources often target younger populations and overlook the unique needs of older adults. |
| Social Isolation Factors | Increased suicide risk among older adults is attributed to social isolation, loneliness, and systemic biases. |
| Call to Action | The study urges for dedicated campaigns and easily accessible resources for older adults in suicide prevention. |
Summary
Suicide prevention for older adults is a critical and urgent issue that needs immediate attention. Given their high risk of suicide, particularly among those 75 and older, it is essential that suicide prevention efforts are tailored to meet the specific needs of this demographic. Current online resources are insufficient and often fail to highlight the unique healthcare requirements facing older individuals. By focusing on creating targeted campaigns and providing accessible information, we can address the alarming trends of suicide in older adults and work towards reducing this public health crisis.