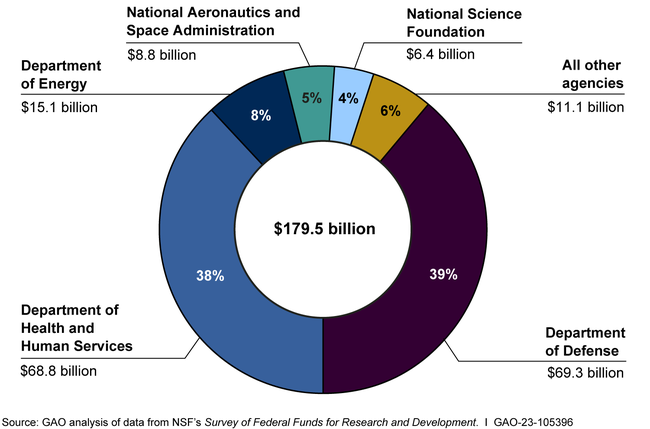
An intriguing connection exists between citrus and depression, highlighting the potential for everyday fruits to influence mental well-being. Recent research suggests that consuming citrus fruits, such as oranges, may significantly reduce the risk of depression by approximately 20%. This discovery stems from the impact of citrus on gut health, specifically in stimulating the growth of beneficial bacteria like *F. prausnitzii*, which in turn supports the gut-brain connection. The improved gut health is thought to facilitate the production of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, known to elevate mood and aid in depression prevention. By understanding the citrus health benefits, we can explore how integrating these fruits into our diets may serve as a simple yet effective strategy for mood enhancement and mental health support.
The relationship between citrus fruits and mental health is gaining attention as researchers delve into dietary impacts on emotional well-being. A notable study indicates that including fruits like oranges in one’s daily intake could play a role in decreasing the likelihood of developing depressive symptoms. This research delves into the intriguing gut-brain interaction, revealing that beneficial gut bacteria such as *F. prausnitzii* may be pivotal in this process. These microbes could influence critical neurotransmitters responsible for regulating mood, offering insight into potential natural remedies for individuals facing emotional challenges. Such findings open up exciting avenues for further exploration into dietary approaches for enhancing psychological health.
The Surprising Link Between Citrus and Depression
Recent research has unveiled a fascinating connection between citrus consumption and a reduced risk of depression. Specifically, a study found that consuming just one medium orange a day may lower the risk of developing depression by approximately 20%. This finding indicates that citrus fruits like oranges may play a vital role in mental health, possibly due to their unique effects on gut bacteria and neurotransmitter production.
The study led by researcher Raaj Mehta highlighted how citrus fruits stimulate the growth of beneficial gut microbiota, specifically *Faecalibacterium prausnitzii* (F. prausnitzii). Increased levels of this essential bacterium were found to correlate with improved mood and lowered depression scores. As serotonin and dopamine levels rise in response to the consumption of citrus, the gut-brain connection becomes even more significant. This suggests that incorporating more citrus into one’s diet could serve as a preventative measure against depression.
Understanding the Gut-Brain Connection
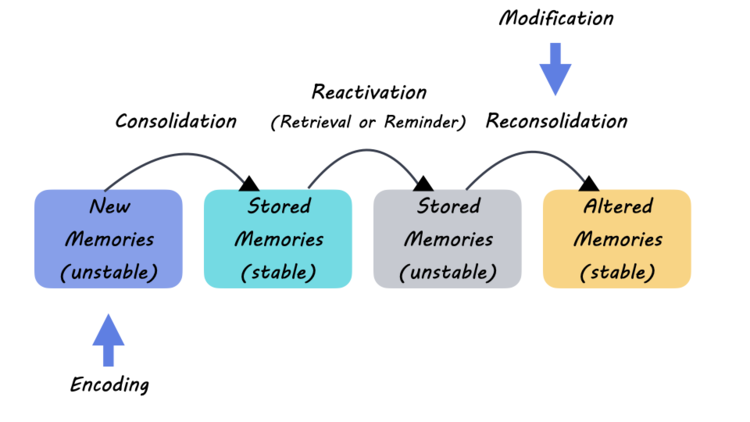
The gut-brain connection is a complex interplay between gastrointestinal health and mental well-being. Emerging studies indicate that the health of our gut microbiome significantly influences mood and cognitive functions. Specifically, the presence of specific bacteria like F. prausnitzii serves as a cornerstone for healthy gut dynamics, reinforcing the positiveness of consuming citrus to promote these beneficial microorganisms.
Your diet, especially one rich in fruits like citrus, can modulate the composition of your gut microbiome. This not only helps improve digestion but is also intertwined with mental health. The positive impact of citrus on the gut flora, through promoting species like F. prausnitzii, highlights the intricate connection between what we eat and how we feel, illustrating the need for further exploration into dietary interventions for mental health.
Citrus Health Benefits You Might Not Know
Citrus fruits are well-known for their high vitamin C content, which is essential for overall health, but their health benefits extend beyond immune support. These vibrant fruits are rich in antioxidants, which can help combat oxidative stress—a factor often linked to mental health issues. Additionally, they contain essential nutrients that bolster the gut-brain connection, aiding in the production of key neurotransmitters that regulate mood.
Furthermore, incorporating citrus fruits into your daily diet may lead to better mental clarity and improved emotional resilience. As research continues to unfold, the mood-elevating properties of citrus are becoming more evident, making them not just a healthy snack but a potential natural remedy for depression prevention. Including citrus varieties such as lemons, limes, and grapefruits can thus diversify your nutrient intake while enhancing your mental well-being.
The Role of F. prausnitzii in Mental Health
*Faecalibacterium prausnitzii* is a flagship species in the human gut microbiome associated with several positive health outcomes. Research indicates that higher levels of F. prausnitzii correlate with lower depression risk and improved overall health. Its role in influencing inflammatory responses, as well as mood regulation through the production of neurotransmitters, positions it as a critical player in maintaining mental health.
Furthermore, dietary interventions that promote the growth of such beneficial bacteria, particularly through the consumption of citrus, can potentially form part of a holistic approach to mental health care. By enhancing the presence of F. prausnitzii via a citrus-rich diet, individuals may not only guard against depression but also foster a healthier gut, home to a balanced microbiome crucial for both physical and mental wellness.
Citrus Fruits as Natural Antidepressants
While traditional antidepressants serve an essential role in treating depression, the potential of citrus fruits as a natural alternative is garnering attention. The unique connection between citrus intake and mood elevation suggests that these fruits could play a complementary role in depression management. The natural compounds found in citrus help to modulate neurotransmitter levels in the brain, potentially leading to mood improvements without the side effects commonly associated with pharmaceuticals.
Incorporating citrus fruits into your diet may provide a low-risk, side-effect-free option for those looking to support their mental health. This approach aligns with growing acknowledgment of the relationship between diet and mood, advocating for the use of whole foods, like citrus, as part of a comprehensive treatment strategy for depression and related mood disorders.
Exploring Clinical Trials for Citrus Effects
As researchers delve deeper into the relationship between diet and mental health, clinical trials regarding the effects of citrus on depression are becoming increasingly pertinent. Evidence suggests that citrus consumption can lead to significant mood enhancements and mood stabilization, warranting further investigation to solidify these claims. Upcoming trials may provide not only validation for the role of citrus in depression prevention but also detailed insights into dosage and individual reactions.
Conducting robust clinical trials could pave the way for new dietary guidelines encouraging the inclusion of citrus in daily diets. With the potential to affect neurotransmitter levels positively, these trials will aim to determine the specific mechanisms by which citrus influences mental health and optimize its benefits for a broad population.
The Significance of Mental Health Nutrition
Nutrition plays an indispensable role in our mental well-being and has emerging importance in the discourse surrounding depression. Diets rich in fruits, especially citrus, could be beneficial in preventing and managing mood disorders. As more studies unveil the connection between nutrition and mental health, the importance of tailoring dietary habits specifically for mental wellness cannot be overstated.
Adopting a diet that encourages the consumption of fruit, with citrus at the forefront, may help improve mental health outcomes. Ensuring a balance of nutrients to support gut health plays a significant role in our overall mood and mental clarity, emphasizing the need for dietary considerations in therapeutic practices.
How Citrus Fits into Holistic Health Approaches
In holistic health paradigms, the emphasis is on treating the whole person rather than isolated symptoms, signaling the importance of dietary habits alongside traditional medical treatments. Citrus fruits, with their myriad of health benefits, can easily be integrated into these approaches, promoting both physical and mental well-being. Including a variety of citrus in one’s diet that emphasizes the gut-brain connection can support comprehensive health and wellness regimes.
Nutrition forms a fundamental pillar of holistic health, influencing mood, energy levels and overall well-being. By recognizing the multifaceted benefits of citrus, practitioners can advocate for dietary recommendations that enhance mental health alongside physical health, illustrating how simple changes can yield profound differences.
Future Research Directions on Citrus and Depression
The rapid evolution of research linking diet and mental health has set the stage for exciting future investigations into the role of citrus in depression and mood disorders. With ample evidence backing the unique effects of citrus on the gut microbiome, particularly the promotion of F. prausnitzii, future studies might explore how varying types of citrus could yield different outcomes in clinical and community health settings.
Moreover, drawing multidisciplinary perspectives that incorporate nutritionists, mental health professionals, and microbiologists could elevate our understanding of how dietary choices impact mental health. By prioritizing the research on citrus, we have the potential to discover new and effective methods for depression prevention and management, perhaps even influencing public health practices surrounding diet and mental well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does citrus consumption relate to depression prevention?
New research indicates that eating citrus, such as an orange a day, may lower the risk of developing depression by approximately 20%. This effect is thought to result from citrus’s ability to boost the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, specifically *Faecalibacterium prausnitzii* (F. prausnitzii), which can enhance the production of mood-regulating neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine.
What is the gut-brain connection in relation to citrus and depression?
The gut-brain connection refers to the biochemical signaling between the gastrointestinal tract and the brain. Citrus fruits have been shown to promote the growth of certain gut bacteria, such as *F. prausnitzii*, which positively influence mood and mental health. This connection emphasizes how our diet, particularly citrus consumption, may play a vital role in depression elevation and prevention.
Can eating citrus improve your mood and prevent depression?
Yes, consuming citrus can improve mood by helping to lower depression risk. Studies suggest that a daily intake of citrus, particularly oranges, supports the growth of *F. prausnitzii* in the gut, leading to increased levels of serotonin and dopamine, neurotransmitters that are crucial for mood regulation and overall mental well-being.
What role does *F. prausnitzii* play in mental health related to citrus intake?
*Faecalibacterium prausnitzii* (F. prausnitzii) is a beneficial gut bacterium associated with mental health. Increased citrus intake has been linked to higher levels of this bacteria, which may help elevate mood and reduce depression risk by enhancing the production of key neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine.
What are the health benefits of citrus beyond mood elevation?
Citrus fruits offer numerous health benefits beyond mood elevation, including high vitamin C content, which boosts the immune system, and antioxidants that may reduce inflammation. Additionally, their consumption has been linked to improved gut health due to the stimulation of beneficial bacteria like *F. prausnitzii*, potentially leading to better overall well-being.
How might citrus act as a supplementary treatment for depression?
While citrus consumption, such as eating oranges, cannot replace traditional antidepressants, its beneficial effects on gut microbiota and mood regulation suggest it could be a supplementary treatment. Future research might reveal how incorporating citrus into one’s diet can aid in depression management alongside other therapeutic approaches.
| Key Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Eating citrus lowers depression risk | A study found that consuming one medium orange daily may reduce depression risk by 20%. |
| Impact on gut bacteria | Citrus consumption is linked to higher levels of *F. prausnitzii*, a gut bacterium associated with mental health. |
| Role of neurotransmitters | *F. prausnitzii* may influence serotonin and dopamine levels, which regulate mood and digestive health. |
| Need for further research | More studies are required to confirm these findings and explore citrus as a part of broader depression management strategies. |
| Future implications | Exploring dietary approaches can enhance mental health understandings and potentially provide simple treatments for depression. |
Summary
Citrus and depression are interconnected, as emerging research suggests that eating citrus, particularly oranges, can significantly lower the risk of depression. By consuming citrus fruits, individuals may benefit from an increase in gut bacteria linked to better mental health, which can influence mood-regulating neurotransmitters. This novel approach to preventing and managing depression presents a promising avenue for enhancing mental wellness through dietary choices.